Over the last two decades the laboratory at AFBI Hillsborough has analysed over 80,000 grass silage samples from Northern Ireland farms.

Whilst the dry matter content of silage increased over this time, in general, there was little improvement in it’s nutritional quality. Grass silage is an extremely important feedstuff in local livestock systems and the absence of an improvement in its quality is considered a missed opportunity. In order to address this AFBI is leading a major DAERA and AgriSearch co-funded research project which is seeking to bring a renewed focus on grass silage quality.
Initial work within this project has focused on understanding the diversity of management practices and decisions taken on commercial farms when making silage. In total, 174 dairy farmers took part in a survey while attending the CAFRE Dairy Open Days at Greenmount earlier this year. A summary of the key findings from the survey are:
General silage making practices:
- 22% of farmers take two cuts of silage, 65% take three cuts and only 13% take four or five cuts.
- A self-propelled forage harvester was used on 63% of farms, while a trailed harvester was used on 17% of farms. A forage wagon (13%) or big bales (7%) was used on a smaller numbers of farms.
- Almost two thirds of farmers (62%) normally use a contractor while 29% never use a contractor. The remaining farmers (9%) sometimes use a contractor.
- Additives are normally used by 47% of farmers, while 35% of farmers never use an additive, with 18% of farmers sometimes using an additive.
- Of farmers who use a contractor, 89% are charged per acre and 7% ‘per bale’. Three farmers (2.4%) are charged per hour, while one farmer was charged on the basis of yield of herbage.
- If contractors were to offer an alternative ‘yield based’ charging system, 64% of farmers said that this might encourage them to cut earlier, while 36% of farmers said it would not.
Factors that farmers perceive to influence silage quality
Farmers were then asked to quantify the impact of a range of factors on the quality of the silage that they made. The impact was quantified as ‘none’, ‘some’, ‘moderate’, ‘large’ and ‘very large’.
Factors relating to timing of silage making are presented in Table 1. As expected, weather related issues, and their impact on timing of silage making, were identified as having the largest impact on silage quality, with 68% of farmers indicating that delaying harvest due to adverse weather or ground conditions had either a large or very large effect on silage quality. Similarly, 53% of farmers indicated that delayed lifting of the crop due to adverse weather or ground conditions had either a large or very large effect on silage quality.
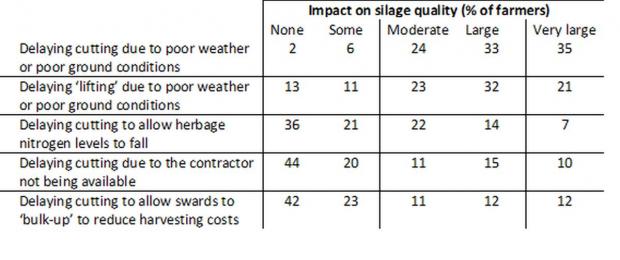
The other key factors affecting silage quality were largely related to ensiling practices, and these are summarised in Table 2. Ensiling grass that grew in the late autumn/early winter, along with first cut silage the following spring, was identified as having either a large or very large effect on silage quality on approximately 30% of farms.
With regard to the quality of grass being ensiled, the impact of poor quality swards was acknowledged as being an issue, with this a particular problem on land taken on conacre where farmers are not prepared to invest in sward improvement. There is clear evidence from research that contamination of crops with either slurry residues or soil can have an adverse effect on silage quality, with this identified as having a large to very large effect on silage quality on just under 25% of farms. While inadequate compaction of silos due to rapid filling, together with inadequate labour available at silage making time, were recognised to have an impact, few farmers perceived this as having a very large impact on silage quality.

Farmers’ views on changes in silage quality over the last 10 years
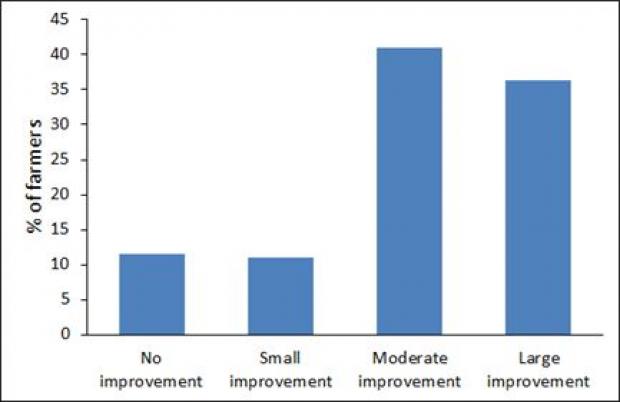
Farmers were then asked if they believed that the quality of silage made on their farms had changed over the last ten years. The results summarised in Figure 1 show that 23% of farmers indicated that there had been either ‘no improvement’ or only a ‘small improvement’ in silage quality, 41% declared that there had been a ‘moderate’ improvement, and 36% reported that there had been a ‘large improvement’. Those farmers that reported an improvement were then asked to highlight the main reason for this. While many factors had contributed to improvements in silage quality, the predominant reasons were ‘earlier cutting’ (43% of farmers) and harvesting better quality swards (22% of farmers). Factors such as attention to detail, wilting, better use of slurry and improved machinery, were also among the reasons given. In view of the importance of earlier cutting in improving silage quality, multi-cut systems will be examined within the current research project.
Conclusions
This survey has highlighted that a diverse range of silage making practices are adopted on local dairy farms. While many factors were identified as having a detrimental effect on silage quality, weather related issues were recognised as having the largest overall effect. Given that many of the other factors identified as impacting on silage quality can be overcome through the adoption of improved management techniques, there is considerable scope to improve silage quality on many farms. On farms where the silage quality was reported to have improved over the last decade, this was primarily attributed to earlier cutting and the ensiling of better quality swards.
Latest news
- AFBI issues Nematodirus warning – Spring 2025 11 April 2025
- Managing Nature Based Risks to the UK Economy and Opportunities for Green Finance 08 April 2025
- AFBI Hillsborough host AERA committee 27 March 2025
- The Omics Days Conference 27 March 2025
